The Polish Patent Office granted a new patent to IPPT PAN. Its authors work at the Department of Experimental Mechanics, IPPT PAN: prof. Zbigniew L. Kowalewski, Dominik Kukla PhD, Mirosław Wyszkowski Eng, Adam Brodecki MSc, and Mateusz Kopeć PhD.
Patent title: Stand for the strength testing of turbine blades subjected to high-temperature cyclic loading conditions under complex stress state and the turbine blades assembly in this stand
The essence of the invention is a stand for testing the strength of turbine blades under conditions of high-temperature cyclic loading and a complex state of stress, fixed in the jaws of a testing machine, containing a gripper assembly for fixing the blade. This assembly consists of two parts, where the upper part is a body with a cuboidal fastening part fixing the body to the upper jaw of the testing machine from above, and the lower part of the stand mounted in the lower jaw of the testing machine is a pusher, which is a rod with the spherical end of a defined radius. The body gripping assembly consists of an adapter mounted in the body in which the turbine blade is mounted, locking plates mounted on both sides of the body at the height of the adapter and screwed together by screws, a side screw pressing the adapter from the side opposite with respect to mounting, and centering and fixing screws of the assembly grippers located on the bottom of the body; the body being substantially cuboidal with a stepped cut-out on the mounting side of the turbine blade in the adapter.
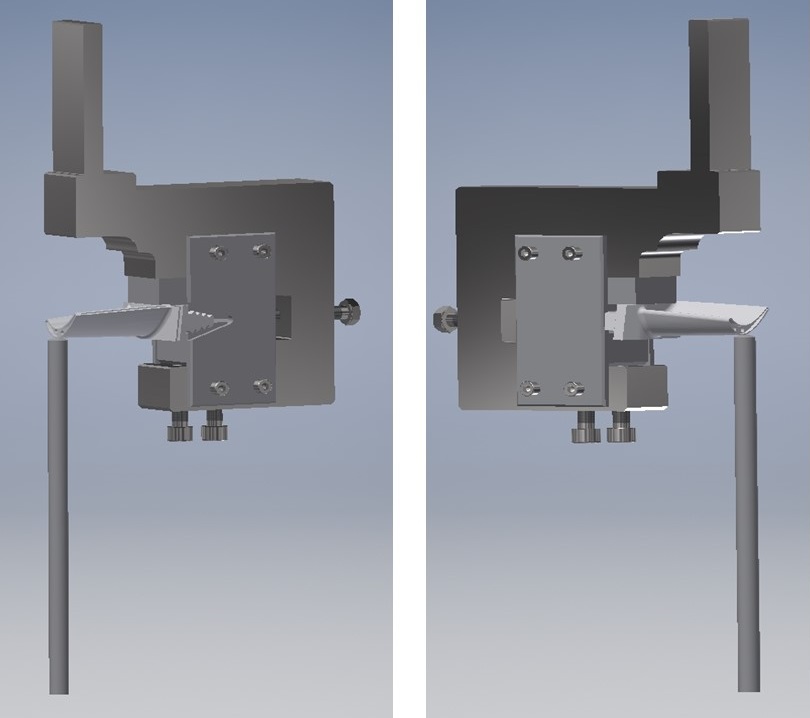
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of the grip with blade, both sides view.
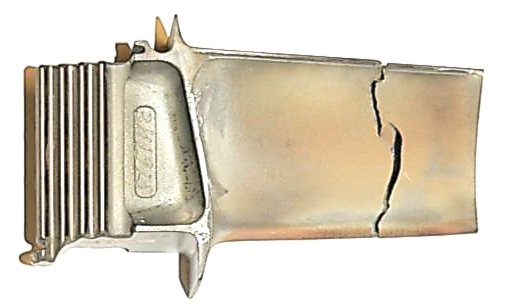
The grip for cyclic loading is dedicated to hydraulic testing machines. It was developed for the needs of the project with the participation of the Military Technical University, Warsaw University of Technology, and the Military Aviation Works. Cycles of fatigue tests were applied to the series of turbine blades until crack initiation (Fig. 2a), and total fracture of the blade appeared (Fig. 2b).

a)b)
Fig. 2. Blades after fatigue tests carried out up to: (a) crack initiation; and (b) total fracture
Figure 3 shows a developing crack of the turbine blade in the patented grip close to the lock base.
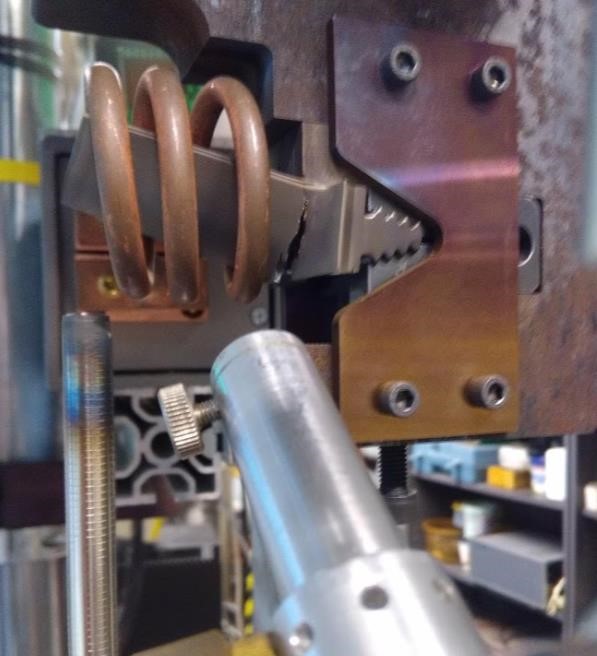

Fig. 3. A view of the fracture development of the turbine blade during fatigue testing. The foreground shows laser pyrometer to control temperatures during tests
The results obtained thanks to the patented grip were published under the title “A Novel Method for High Temperature Fatigue Testing of Nickel Superalloy Turbine Blades with Additional NDT Diagnostics”, written by its designers and patent holders: Dominik Kukla 1, Mateusz Kopec 1,2, Ryszard Sitek 3, Aleksander Olejnik 4, Stanisław Kachel 4 and Łukasz Kiszkowiak 4.
1 Institute of Fundamental Technological Research, Polish Academy of Sciences, Pawińskiego 5B, 02‐106 Warsaw, Poland; (D.K.); (M.K.)
2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK
3 Faculty of Materials Science and Engineering, Warsaw University of Technology, Wołoska 141, 02‐507 Warsaw, Poland;
4 Faculty of Mechatronics Armament and Aerospace, Military University of Technology, 2 gen. Sylwestra Kaliskiego Str., 00‐908 Warsaw, Poland; (A.O.); (S.K.)


















