Researchers at IPPT PAN have advanced the understanding of how our bodies defend against common respiratory infections caused by RNA-viruses like influenza A/B, RSV, or SARS-CoV-2. In infected cells, viral RNA triggers the synthesis and secretion of interferon (IFN) β, which reaches neighboring not-yet-infected cells and warns them about a nearby threat. This cell-to-cell communication constitutes one of crucial mechanisms of our innate immunity.
Using a chemical analog of viral RNA, poly(I:C), researchers from IPPT PAN demonstrated that non-self RNA first activates and then terminates interferon-induced antiviral responses. Activation has been previously known to involve STAT1/2 signaling, whereas the molecular mechanism responsible for switching off the interferon-induced signaling was discovered to be the depletion of the IFN-β receptor, IFNAR. It was shown that the IFNAR depletion is a consequence of a protective “shutdown”, during which infected cell’s RNAs are massively degraded and protein biosynthesis is halted. A side effect of this “shutdown” is downregulation of inhibitors of NF-κB and IRF3. After these two transcription factors escape from the control of their inhibitors, they jointly trigger the synthesis of IFNβ (mRNA of which was found to be exceptionally “shutdown”-resistant). Taken together, this research demonstrates that and explains how the chemical analog of viral RNA turns cells from interferon responders to interferon producers.
This finding, together with detailed experimental characterization of the kinetics of mRNAs and proteins involved in the innate immune response, led to the formulation of a comprehensive mathematical model of the innate immune signaling. The ODE-based model incorporates five interlinked regulatory modules (see figure below) and results from systematic simplifications, which allowed to achieve parameter identifiability.
This research is a follow-up of the study by Czerkies et al. published in 2018 in Nature Communications (doi:10.1038/s41467-017-02640-8). Results of the current research by Korwek et al. were just published in Science Signaling (doi:10.1126/scisignal.abq1173).
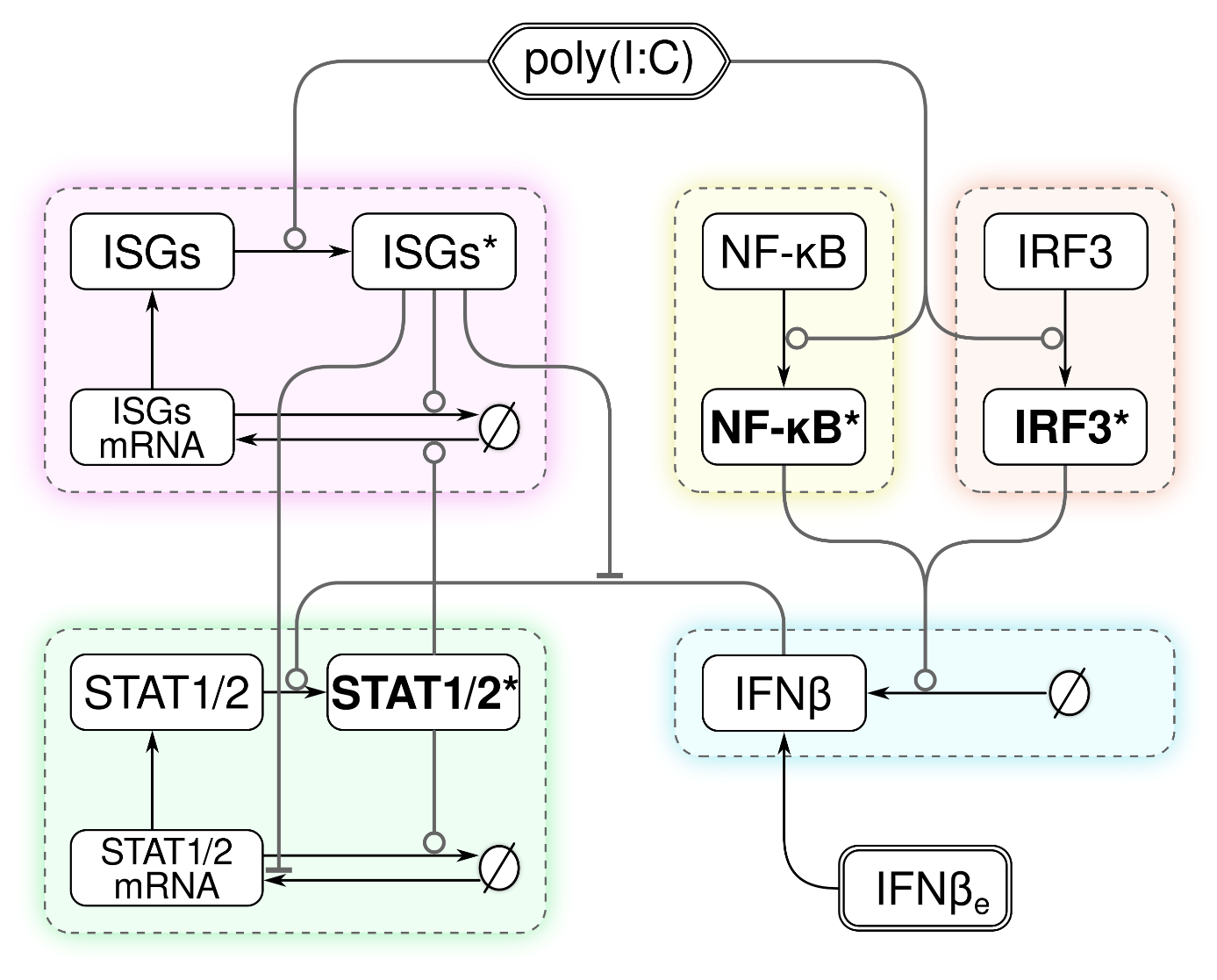
Fig.: Coarse-grained scheme of the computational model of innate immune signaling triggered by viral RNA or its analog, poly(I:C), showing key interactions between the five regulatory modules studied experimentally to develop the model.


















